51,000+
International Patient Treated
91
Countries Treated
10+
Years Treating International PatientsWhy Choose Wockhardt Hospitals for Cancer Treatment?
- Internationally trained doctors with UK/US fellowship.
- Treated more than 2000 cancer patients from Africa, the Middle East, South Asia, Europe, and USA in last 10 years
- High success rate.
- Specialized doctors for Breast Cancer, Gastrointestinal Cancer, Thoracic Cancer, Urologic Cancer, Gynecologic Cancer, Head and Neck Cancer, Blood Cancer, Chemotherapy, Radiation, etc.
- No waiting time.
- Affordable cost compared to others.
Life Wins Stories
I would like to emphasis that the requested medical services has been delivered and we appreciate your great efforts. Most importantly Dr. Mazda Turel and his entire team, Mr. Saurabh Pal, Ms. Heena, Mr. Jeev, the staff & nurses on level 18, speech therapists, physio team and ICU team.I would like to emphasis that the requested medical services has been delivered and we appreciate your great efforts. Most importantly Dr. Mazda Turel and his entire team, Mr. Saurabh Pal, Ms. Heena, Mr. Jeev, the staff & nurses on level 18, speech therapists, physio team and ICU team.
Renowned Doctors
at Wockhardt Hospitals

Dr. Jimmy Mirani
Consultant – Medical Oncology
Medical OncologySouth Mumbai - Mumbai Central

Dr. Atul Naryankar
Consultant Medical Oncology
Cancer Care, Medical Oncology, Oncologists Cancer DoctorsNorth Mumbai – Mira Road

Dr. Jeyhan Dhabhar
Consultant Medical Oncologist
Medical Oncology , OncologySouth Mumbai - Mumbai Central
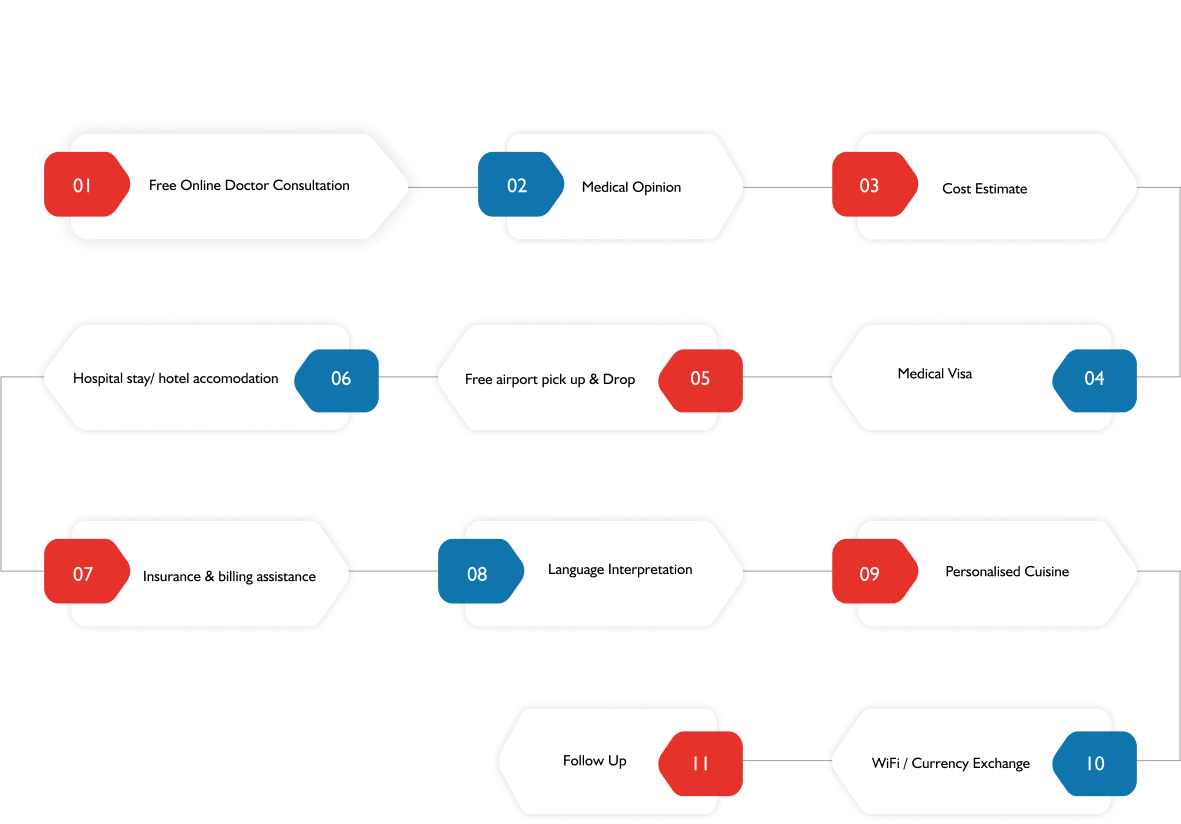
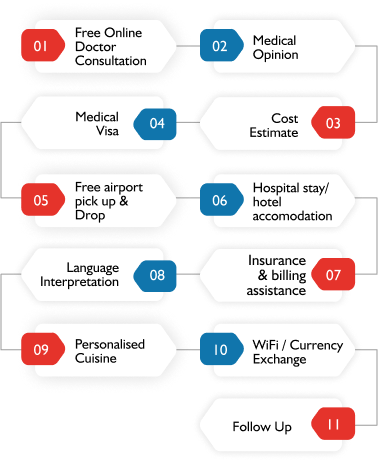
End-to-End Patient Care Services
Symptoms & Causes Of Cancer Care Problems
The causes of cancer can vary largely from obesity to radiation exposure. It is better to have knowledge of the causes and symptoms related to cancer. Depending on whatever area of the body is affected, cancer can create different signs and symptoms.
General indications and symptoms that are connected to cancer but not exclusive to it include:
- Fatigue
- A thick spot or lump beneath the skin’s surface
- Changes in weight, including inadvertent gain or loss
- Chronic, inexplicable pain in the muscles or joints
- Chronic coughing or breathing difficulties
- Alterations in bowel or bladder routines
- Persistent heartburn or pain following a meal
- Inexplicable bruises or bleeding