What is the importance of the Kidney and its functions?
- The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs situated in the back muscles (on either side of the spine) of the upper abdominal cavity in our body.
- The main function of the kidney is to filter the blood circulating through your body by removing waste and excess salts and regulate the water fluid levels.
- They are also responsible for regulating pH, salt, and potassium levels in the body.
- Produce hormones that regulate blood pressure and control the production of red blood cells.
- Activate a form of vitamin D that helps the body absorb calcium.
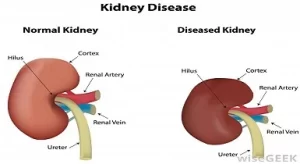
What are some of the Kidney Diseases?
1) Chronic Kidney Disease
- The most common form of kidney disease is chronic kidney disease caused by high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Kidney failure is the last (most severe) stage of chronic kidney disease. This called end-stage renal disease or ESRD for short.
- Other causes include, autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and IgA nephropathy, Genetic diseases, polycystic kidney disease, Nephrotic syndrome and Urinary tract problems
What is kidney failure?
Acute Renal Failure:
- This type of kidney failure is called acute kidney injury or acute renal failure and is of sudden onset. .
- Common causes of acute renal failure include Heart attack, Illegal drug use and drug abuse, not enough blood flowing to the kidneys, Urinary tract problems. However this type of kidney failure is not always permanent.
What is chronic renal failure?
Chronic kidney disease, also known as chronic renal failure, is a slow progressive loss of kidney function over a period of several years. Eventually the patient has permanent kidney failure. It is staged as per based on the patient’s level of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) which is a measure of filtering capacity of the kidneys.
What are the common symptoms of kidney failure?
- Nausea
- vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Changes in urine output
- Fluid retention
- Anaemia (a decrease in red blood cells)
- decreased sex drive
- Sudden rise in potassium levels (hyperkalaemia)
- Inflammation of the pericardium (fluid-filled sac that covers the heart
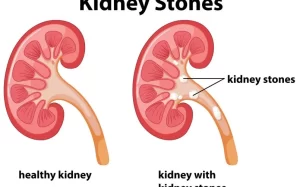
What is kidney stone?
A kidney stone is a hard, crystalline mineral material formed within the kidney or urinary tract.
Kidney stones form when there is a decrease in urine volume and/or an excess of stone-forming substances in the urine. Dehydration is a major risk factor for kidney stone formation.
What are the symptoms of kidney stone?
Symptoms of a kidney stone include flank pain and blood in the urine can be present.
What is the diagnosis for kidney stones?
Diagnosis of kidney stones is best accomplished using an ultrasound, intravenous pyelography (IVP), or a CT scan.
What is the treatment of kidney stones?
Most kidney stones eventually pass through the urinary tract on their own within 48 hours, with ample fluid intake.
Ketorolac (Toradol), an injectable anti-inflammatory drug, and narcotics may be used for pain control when over-the-counter pain control medications are not effective.
Lithotripsy is a procedure which can be done to remove stones. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) is a non-invasive treatment of kidney stones and biliary calculi.
What are kidney infections?
Kidney infections are caused when bacteria infects your kidneys. The bacteria are usually a type called E. coli, which live in the intestine. The bacteria get in through the opening of the urethra and move upwards through the urinary tract, first infecting your bladder and then your kidneys.
Most urinary tract infections involve only the bladder and urethra (the lower urinary system). Pyelonephritis results when a UTI progresses to involve the upper urinary system (the kidneys and ureters).
What are the signs and symptoms of kidney infections?
Fever, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, and confusion.
A Kidney abscesses can occur where pus accumulates inside kidney tissues. Symptoms include blood in urine, weight loss, and abdominal pain.
What are the various investigations carried out for kidney diseases?
Urine output measurements. The amount of urine excreted in a day may help to determine the cause of kidney failure.
Urine tests: Analysing a sample of urine, a procedure called urinalysis, may reveal abnormalities that suggest kidney failure.
Blood tests: A sample of blood may reveal rapidly rising levels of urea and creatinine — two substances used to measure kidney function.
Imaging tests. Imaging tests such as ultrasound and computerized tomography may be used to help see your kidneys.
Kidney biopsy: Removing a sample of kidney tissue for testing, a kidney biopsy to remove a small sample of kidney tissue for lab testing.
What is Kidney Transplant?
- A kidney transplant is a surgical procedure which allows a person whose own kidneys have failed to receive a new kidney (recipient) from another person. (Donor)
- A successful kidney transplant can improve many of the complications of kidney failure and is the best solution to patients whose kidneys have stopped working or are close to failing.
- The functioning kidney is removed either from a living donor or someone who has recently passed away.
- A transplanted kidney performs all the functions of a kidney a person has from birth
What is the most common medical indication for kidney transplant?
- Patient who is diagnosed with end stage kidney diseases is candidates for kidney transplantation. In other words the kidneys are not functioning optimally.
- The two basic options for treating end-stage kidney failure are dialysis and kidney transplantation.
What are the types of kidney transplants available?
A) Living donor transplant: Become a Donor Today & Save a Life!
A living donor may be someone in your immediate or extended family, or it may be your spouse or a close friend. In some cases, a living donor may even be a stranger who wishes to donate a kidney to someone in need of a transplant.
Advantages of Live Donor Transplant are as follows:
- Receiving a kidney from a living donor has shown to last longer than a kidney from a deceased donor.
- The operation can be planned to suit your schedule, since it is not necessary to wait for a kidney to become available from a deceased donor.
B) Deceased donor (cadaver donor) is someone who has consented to donating his or her organs upon death. In situations where the wishes of the deceased donor are not known, family members may consent to organ donation.
What are the investigations which indicate that kidney transplant is required?
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the best measure of kidney function and these determine the stages of kidney disease in patients:
Stage 5 End Stage CKD (GFR <15 mL/min) – INDICATOR FOR TRANSPLANT
2) Creatinine levels: when kidneys are working well they remove creatinine from the blood. As kidney function slows, blood levels of creatinine rise are also another indicator.
- When is a patient advised for kidney transplant?
A person is advised kidney transplant in the following conditions”
Kidney Failure – Temporary (AKI Acute Kidney Failure)
– Permanent (CKD Chronic Kidney Disease
2) What is the treatment option a patient has for kidney failure?
The three treatment options Renal Replacement therapy.
Haemodialysis
Peritoneal Dialyses
Renal Transplantation for treating kidney
What are the benefits of kidney transplant vs dialysis?
The main benefit of successful kidney transplant offers a better quality of life than dialysis. This is because a transplant allows for:
- Considerably greater freedom (no need to spend time on dialysis),
- increased energy levels,
- Less restricted diet.
- In addition, studies have shown that people who receive kidney transplants live longer than those who remain on dialysis.
Who can be a living donor?
A living donor may be a family member, friend, co-worker, neighbour, or even a complete stranger, as long as they are a medical compatible for you.
What is the precondition for a living donor?
- All living donors must make a free and independent choice.
- They must understand the medical risks to donating a kidney.
- Living donors will have a number of medical tests to help ensure they are healthy enough to donate.
- Both the donor and the patient should have the same blood group.
- The donor has to be less than 50 years of age, body mass index of less than 25.
- Preferably the donor should be a near relative of the recipient (1st relative).
- If he is not a first relative (non-relational donor), the most important criteria is that the donor must donate the section of his liver ‘Voluntarily’ and “Out of Affection” to be legally compliable.
- Also a PATIENT who is not having Prior kidney Disease. AND is not Loosing Protein in Urine or has a history of Angioplasty or Bypass surgery
- Donor must be neurologically & mentally fit to understand the procedure and indications
The gift of saving a human life is probably the most compassionate deed of all, where you can give or receive a second chance to normal and healthy life.
As part of our endeavour to create awareness on different health issues we would like to provide you information on a life-giving procedure carried out at Wockhardt Hospitals.
For any queries regarding kidney infections and kidney transplant please contact Wockhardt Hospital.
Wockhardt Hospitals, a chain of tertiary care super-specialty hospitals has more than 25 years of experience in the creation and management of Super Specialty Hospitals in India. We are a premiere hospital in the country specializing in the treatment of digestive disorders. We provide comprehensive digestive care to our patient’s .Our Nephrology department is regarded, as one of the centres for excellence. Our clinical expertise and infrastructure support the treatment of health conditions, related to all kidney disorders.
At Wockhardt Hospitals, Our philosophy is to serve and enrich the quality of life of our patients giving them a winning edge to live life to the fullest. The gift of saving a human life is probably the most compassionate deed of all, where you can give or receive a second chance to normal and healthy life. As part of this endeavour the Renal Replacement therapy program has been initiated where, Haemodialysis Peritoneal Dialyses, Renal Transplantation form part of treatment modalities for kidney disease in chronic renal failure patients. We have already achieved many successful transplants already and provided a better quality of life to patients suffering from terminal kidney diseases. Our hospitals have a full-fledged dialysis unit, intensive care facility and full integrated operation theatre with advanced equipped to carry out super speciality surgery like renal transplantation. All infection control protocols, quality nursing care, advanced clinical acumen, Facilities and services are as per international standards and help to facilitate treatment and recuperation of our transplant patients.
Wockhardt Hospitals is regarded as a centre of excellence the healthcare domain, having facilities in North Mumbai (Mira road), South Mumbai (Mumbai Central), Navi Mumbai (Vashi), Nagpur, Nasik, Rajkot and Surat. Wockhardt Hospitals has state-of-the-art infrastructure. Our prime objective is patient safety and quality of care at all levels. The guiding philosophy is to serve and enrich the Quality of Life of patients and to make life win.