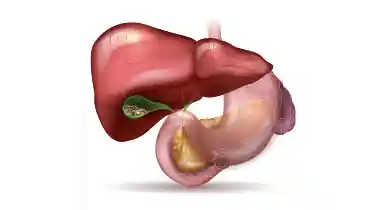
Gallstones are formed from bile cholesterol and bilirubin in the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small saclike organ in the upper right part of the abdomen, just below the on the right side. It forms part of the biliary system, which includes the liver and the pancreas. The gall bladder stores bile and digestive enzymes. Generally they don’t cause issues, however if there are many stone in gallbladder or they become large in size. Gallstones can cause the blockage of the bile duct which can cause inflammation and ultimately severe pain, infection, and organ damage due to gall bladder stones.
There are two types of gallstones:
These stones in the gall bladder can be either
- Cholesterol stones and
- Pigment stones.
What causes Gallstones?
- Cholesterol or bilirubin in the bile is high can cause gall bladder stones.
- Other substances in the bile may promote the formation of stones in the gall bladder.
- Liver disease or blood disease causing have high levels of bilirubin can cause stones in gall bladder.
- Poor muscle tone may keep the gallbladder from emptying completely. The presence of residual bile may promote the formation of gallstones in.
- Obesity or losing a lot of weight quickly on diet therapy
- Certain medications such as birth control pills or cholesterol lowering drugs.
- Diet with large amounts of cholesterol and other fats increases the risk of gallstones,
What are symptoms of gallstones?
Most people with gallstones have no symptoms.
The most common symptom is pain in the right upper part of the abdomen. The pain usually starts within 30 minutes after a fatty or greasy meal. The pain is usually severe, dull, and constant, it the pain can radiate to the right shoulder or back. Pain generally occurs at night and can cause a lot of discomfort. Other common symptoms of gallstones include the following nausea and vomiting, fever, indigestion, belching, bloating and jaundice.
Gallstones Diagnosis
Ultrasound is the best test to examine the gallbladder for stones. An alternative to ultrasound is an oral cholecystogram can be advised. Both ultrasound and OCG can detect gallstones in the gallbladder about 95% of the time.
An X-ray is taken of the gallbladder after the patient swallows pills containing a safe, temporary dye. The dye helps the gallbladder and gallstones show up better on the X-ray.
Other tests include:
- Cholescintigraphy (HIDA scan)
- CT scan: It shows the gallbladder and the biliary ducts and can detect gallstones, blockages, and other complications.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A thin, flexible endoscope is used to view parts of the patient’s biliary system.
Treatment of Gallstones:
Gall bladder stone removal:
- Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy (ESWL): A device that generates shock waves is used to break gallstones up into tiny pieces .These tiny pieces can pass through the biliary system without causing blockages. This is usually done in conjunction with ERCP to remove some. Gall bladder stone removal. The procedure, which is now rarely performed, has been used for people who have long-term (chronic) inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) and who are not strong enough for surgery. But it is not appropriate in treating sudden (acute) cholecystitis.
- Dissolving stones: These drugs work best for cholesterol stones. Drugs made from bile acids are used to dissolve the gallstones.
- Gallstone Surgery (Cholecystectomy) or Gall bladder stone operation
- Surgical removal of the gallbladder and is the usual treatment for symptomatic or complicated gallstones in treatment of gall stones.
- Laparoscopic removal or gallbladder stones operation: Nowadays gallbladders are removed by laparoscopic cholecystectomy. In this procedure the gallbladder is removed through a small slit in the abdomen using small tube-like instruments called a laparoscope. It is a tube-like instrument having a camera and surgical instruments attached, which are used to take out the gallbladder with the stones inside it.
- This procedure of removal of gall bladder is painless as compared to GALL BLADDER removal surgery
- This types of gall stones removal surgery is less likely to cause less complications, and has a faster recovery time.
- A laparoscopic procedure for treatment for gallstones, is preferred if it is appropriate for the patient. This type of gallbladder removal surgery is done under general anaesthesia and usually takes 20 minutes to one hour.
- Gallbladder removal surgery: The gallbladder is sometimes removed through a 3 to 6 inch incision in the right upper abdomen in this gallbladder surgery. The most common reasons for doing an open gallbladder surgery FOR Gallbladder removal is infection in the biliary tract and scars from previous surgeries. This type of gallstones surgery is performed in the operating room with the patient under general anaesthesia.
Occasionally, ERCP is done just before or during gall bladder surgery to locate any gallstones that have left the gallbladder and are located elsewhere in the biliary system. These can be removed at the same time as gallbladder stones surgery, eliminating the risk that they might cause a complication in the future
- Role of diet is essential in the treatment of Gall stones.
In case you are experiencing any of signs or symptoms related to GALL BALDDER stone and would like to know treatment of gall stones, gallbladder surgery, and removal of stones in gall bladder or would also like to know more details about digestive care disorders, please contact our centres at Wockhardt Hospital. Wockhardt Hospitals is one of the countries premium hospitals that are focused on the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of digestive diseases and illnesses.
Wockhardt Hospitals, a chain of tertiary care super-specialty hospitals has more than 25 years of experience in the creation and management of Super Specialty Hospitals in India.
We are a premiere hospital in the country specializing in the treatment of digestive disorders. We provide comprehensive digestive care to our patients. Our Gastroenterology Surgery and Minimal Invasive Surgery Department at Wockhardt Hospitals are regarded, as one of the centres for excellence. Our clinical expertise and infrastructure support the treatment of health conditions, needing laparoscopic surgery or general surgery. For further information visit Digestive Care Speciality at Wockhardt Hospital.
Wockhardt Hospitals is regarded as a centre of excellence the healthcare domain, having facilities in North Mumbai (Mira road), South Mumbai (Mumbai Central), Navi Mumbai (Vashi), Nagpur, Nasik, Rajkot and Surat. Wockhardt Hospitals has state-of-the-art infrastructure. Our prime objective is patient safety and quality of care at all levels. The guiding philosophy is to serve and enrich the Quality of Life of patients and to make life win.